Porcelain Veneers in Sugar Land, TX
Do you have chipped, dark, discolored, or unevenly spaced teeth? If so, you may want to consider dental veneers from SmileTexas®. Dental veneers are a fast, effective, and popular cosmetic dental solution to fix your teeth and give you the beautiful smile you deserve.
Our highly trained team of cosmetic dentists, located in Sugar Land, Texas, specializes in creating top-notch smiles. With years of experience and credentials from leading dental institutions, our team ensures exceptional results.
Get The Healthy, Beautiful Smile
You Want In Just 2 office visits!

Schedule a Consultation Today!
What Are Dental Veneers?
Dental veneers are thin shells of porcelain bonded to the front of the tooth. Veneers are an ideal way to correct stained, spaced, chipped, or crooked teeth. In just two visits, veneers will transform your smile into a bright, straight, natural-looking smile.
At SmileTexas®, we use porcelain veneers and gentle no-prep veneer alternatives. Porcelain veneers are designed in a style and proportion to fit your face, to look naturally beautiful, and give you a great new smile you’ll be proud to show off. Veneers make your smile straight, white, resistant to staining and discoloring, and in many cases are stronger than your natural teeth. The end result is what we call a “Smile Makeover” because your beautiful, new smile will make you feel more attractive, confident, and like a new you!
View Our Instagram
Error: No connected account.
Please go to the Instagram Feed settings page to connect an account.
How long do porcelain veneers last?
Several factors can influence how long your porcelain veneers last. These include the quality of the dental porcelain your dentist chooses and how well the veneers fit into the bite. Good oral care is also a factor that affects the lifespan of veneers. Because of the high skill level and vast experience of the dentists at SmileTexas, our porcelain restorations have an amazing fit to the supporting tooth. Further, we only place the very highest quality porcelain from one of the World’s best dental labs. That is why we tell our patients that with proper care there is no time limit as to how long your new smile can last. At SmileTexas®, we have many patients with porcelain veneers that are over twenty years old and still look beautiful! We have been placing all-porcelain veneers and crowns since 2003. We have thousands of patients with veneers that are over fifteen years old and still look amazing!
What Problems Can Porcelain Veneers Fix?
One of the biggest reasons why patients love dental veneers is that they can fix a variety of issues with just one procedure. Dental veneers can:
- Repair small, chipped, or cracked teeth
- Fill in unsightly gaps and spaces
- Cover severe stains or dark colors
- Make your teeth straight and white
Who is an ideal candidate for Dental Veneers?
Dental veneers are an excellent option for many patients. During your initial consultation with our dentists at SmileTexas®, we will perform a brief oral examination to make sure you’re a good candidate for veneers. Typically, patients who are suitable for this procedure have good jaw and oral health, don’t smoke, have moderately straight teeth, and want to fix some cosmetic imperfections.
What Are Dental Veneers Made Of?
Here at SmileTexas®, we offer patients two types of dental veneers: porcelain veneers and no-prep veneers. Porcelain veneers are the most common type of dental veneer and require us to sand down your existing teeth to place them on top. With no-prep veneers, however, they are so thin that we can put them on top of your existing teeth without having to prep them beforehand.
What are Possible Dental Veneer risks?
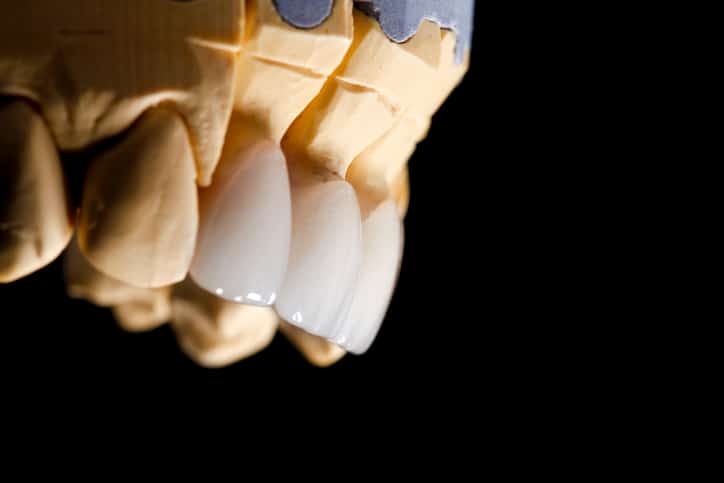 Patients interested in porcelain veneers, even no-prep veneers, should receive this treatment only from a thoroughly trained and highly experienced cosmetic dentist. The training and expertise of the treating dentist is integral to minimizing any potential complications as well as the longevity of your new veneers. Some of the risks associated with porcelain veneer treatment include:
Patients interested in porcelain veneers, even no-prep veneers, should receive this treatment only from a thoroughly trained and highly experienced cosmetic dentist. The training and expertise of the treating dentist is integral to minimizing any potential complications as well as the longevity of your new veneers. Some of the risks associated with porcelain veneer treatment include:
Tooth sensitivity. Regardless of the type of veneers you choose, there is a slight chance that your teeth will be sensitive to hot and cold foods and beverages. If this occurs, it usually resolves itself over a short period of time. Until then, you may use a toothpaste formulated for sensitive teeth.
Poor fit. When you choose SmileTexas for your porcelain veneers, you can expect your dentist to be extremely thorough in making sure your veneers fit perfectly. Poorly fitting veneers are more vulnerable to chips or cracks. They can also create more stress on the jaw by “throwing off” the bite.
Discoloration. Porcelain veneers are highly resistant to staining as they are less porous than a natural tooth. However, patients with veneers should implement the same brushing and flossing habits as with natural teeth for the best results.
Chipping and breakage. Veneers are made to look just like natural, beautiful teeth. However, there is still a risk of chipping or breakage if you chew or bite on hard objects.
Patient Testimonial
veneers before and after
Porcelain Veneer Procedure
Placing Porcelain Veneers properly and effectively is a skill all on its own, and requires precise and artistic talent from a cosmetic dentist. At SmileTexas®, it will take only two, that’s right only two visits to get the smile you want!
What to expect on your first visit?
On your first visit, our doctors will give you a consultation regarding what you are expecting. a lot of points will be discussed such as the shape, size, and even the color of the veneers you want. We will begin preparation on your teeth, and we will give you temporaries until our master ceramist creates your perfect veneers. This process typically takes about two weeks. At your second visit we remove the temporary restoration and your custom-made, beautiful new porcelain veneers are securely bonded to your teeth. Your dazzling new smile is immediately apparent. There is minimal (if any) discomfort after this procedure.
Dr. Bret C. Davis is Houston’s award-winning cosmetic and implant dentist who has helped thousands of clients transform their smiles.
Porcelain Veneers Results
Porcelain veneers are the perfect choice for covering up chips, cracks, and issues with teeth. Because porcelain veneers are custom-made and fitted to your teeth, they are easily customizable and can do more than change the color of your teeth. Crooked and chipped teeth can have their appearances improved to give you a beautiful new smile. porcelain crowns, or caps, that can be color-matched to your veneers are useful for covering up missing teeth and help with other issues.
Take a look at our Smile Gallery, It has a comprehensive list of before and after photos to show you the results of many of our happy patients. We are committed to excellence and feel its important to get a first-hand view of how well veneers look.
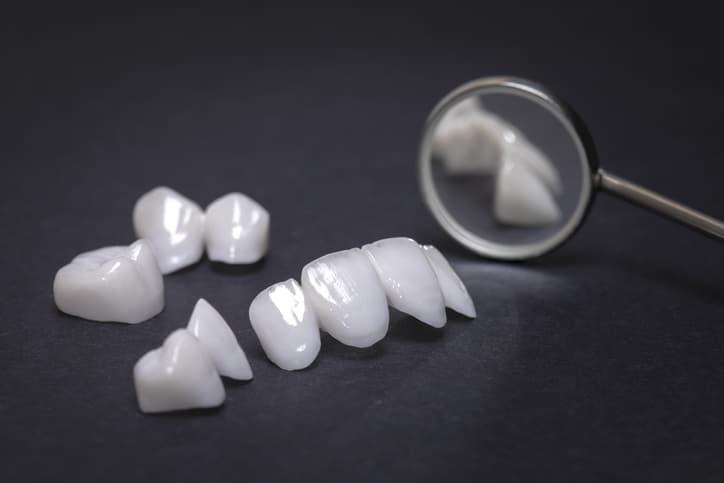
Porcelain Veneers Aftercare Do’s and Don’ts
DO
- Brush and floss your teeth as instructed by your dentist.
- Only bite and chew things you would with natural teeth.
DON’T
- Avoid biting or chewing hard objects.
- Play contact sports without a proper mouth guard.
- Avoid smoking.
How to take care of teeth after getting dental veneers?
While you won’t get a cavity on a veneer, it is possible for tooth decay to develop at the margin of a veneer or on the uncovered back part of a tooth. Good oral care is essential to taking care of teeth and prolonging the life of the veneers. Oral care can involve a soft-bristled toothbrush and nonabrasive toothpaste. Flossing is of the utmost importance to keep debris and bacteria from accumulating around the margins of veneers. Finally, if you have veneers, you should see your dentist every six months. These habits are important for any healthy, beautiful smile.
Dietary Restrictions After Getting Veneers?
There are no dietary restrictions for people with porcelain veneers. We just ask that people consider what they are biting and chewing just as they would with natural teeth. If you can’t get through the morning without that cup of Joe, enjoy! The quality all-porcelain restorations that are placed at SmileTexas are highly resistant to staining from coffee, wine or sodas.
how much do veneers cost?
Many factors contribute to the cost of a Smile Makeover using dental veneers. Things like the number of teeth to be restored, the amount of tooth preparation required, will the bite alignment need to be adjusted by restoring teeth in the back of the mouth, all impact the cost of a procedure. We never want to give an inaccurate quote.
This is why we offer a Complimentary Consultation that includes any necessary X-rays and a thorough exam. At the end of this Free Consultation, we will give you a written, all-inclusive quote that is customized just for you. Rest assured that our fees are extremely competitive and we have amazing financing alternatives. We will try our hardest to help you get the life-changing smile you deserve.
Why Choose SmileTexas®?
SmileTexas® is home to our skilled dentists who create stunning smiles. With over a decade of experience, we’ve has transformed countless lives, helping patients regain the ability to eat, speak, and smile confidently without waiting months for results.
Dr. Bret Davis has completed thousands of Smile Makeovers and full-mouth restorations using advanced techniques. With specialized training from the Las Vegas Institute for Advanced Dental Studies, he brings a level of expertise that is hard to find.
Dr. Mackenzi McAfee-Dooley is passionate about giving people teeth they love through dental implants, veneers, and restorative procedures. At SmileTexas®, we aim to deliver smiles that look great and make life better.
Do I Need To Whiten My Natural Teeth Before Getting Veneers?
Whitening your natural teeth before getting veneers can create a beautiful color match, especially for teeth that won’t be covered by veneers. While veneers are custom-made to match your preferred shade, whitening ensures a brighter smile.
Do Veneers Stain Over Time Like Natural Teeth?
Porcelain veneers are highly resistant to staining because they are less porous than natural teeth. However, it helps to practice good oral hygiene and avoid abrasive toothpaste to keep them looking their best for years to come.
What Happens If A Veneer Gets Damaged Or Comes Off?
If a veneer is damaged or comes off, rest assured that it can typically be repaired or replaced. Working with a skilled cosmetic dentist, like those at SmileTexas®, minimizes the chances of issues occurring. In the rare event of damage, there are temporary options that can keep your smile looking great while your permanent restoration is prepared.
Can Veneers Fix Teeth That Are Significantly Misaligned?
Veneers can improve the appearance of mild misalignment and make your teeth look straighter, but they won’t actually correct the issue. For significant alignment issues, you may need orthodontic treatment before we can place the veneers.
Can I Get Veneers If I Grind My Teeth?
Yes, but it’s important to take measures to protect them. A custom night guard can prevent damage and help your veneers remain intact.
Schedule Your Free Veneer Consultation
To learn more about Porcelain Veneers or to schedule a consultation, call our SmileTexas® Sugarland office at (281) 265-7645. You can also fill out the appointment request form on this page, and our talented staff will help you set up a personalized meeting with Dr. Davis, or Dr. McAfee-Dooley. Our practice looks forward to serving you!
Medical Source click here.
